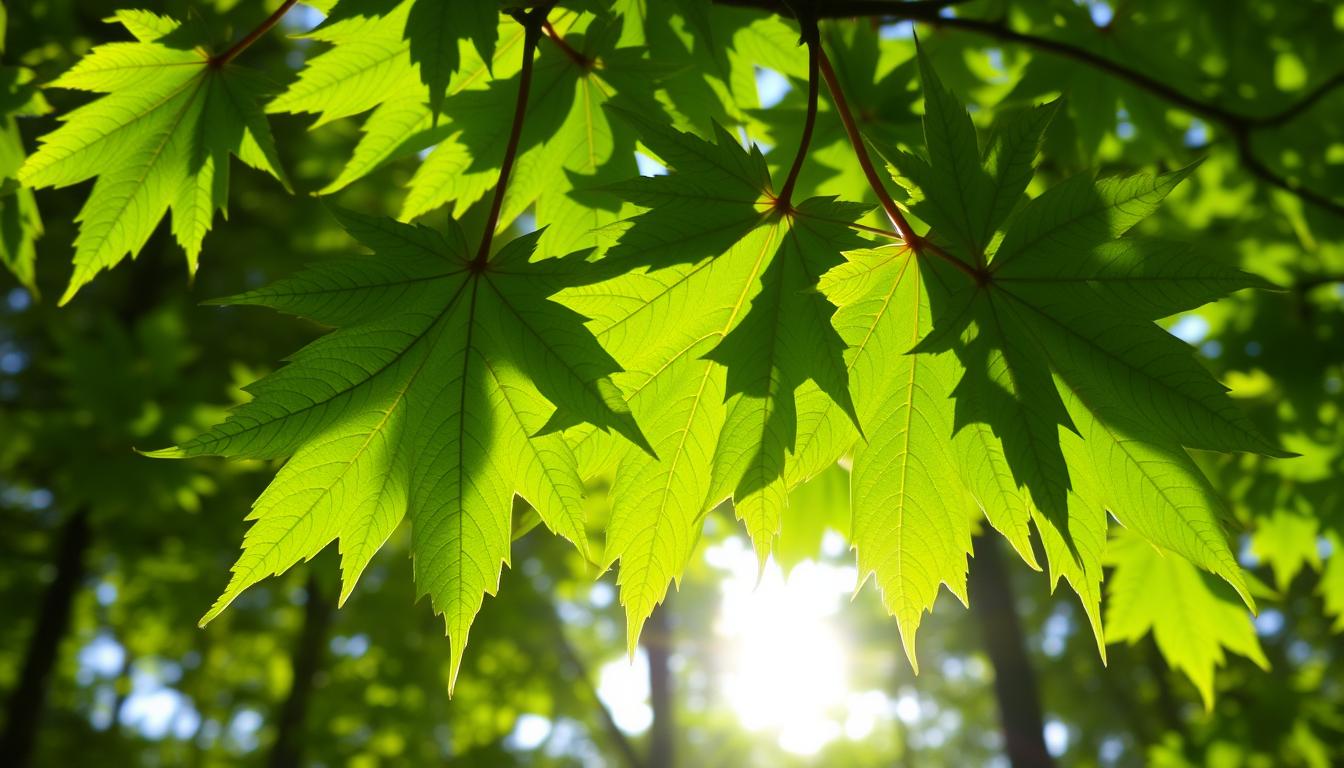
Remembering my grandfather’s advice, I learned to care for maple trees. These trees are not a fair portion of the scene. They live stories of strength, lasting up to 300 years with the right care.
Maple tree leaves tell a story of health and survival. In the fall, they change from green to vibrant oranges and reds, showing the tree’s health.
Knowing how to check maple tree leaves is important. It’s not just about their beauty. It’s about keeping these trees healthy in our gardens and forests. Spotting disease early can save a maple tree.
Table of Contents
Understanding Maple Tree Health Basics
Maple trees are amazing deciduous trees that are key in North American ecosystems and economies. They help with leaf collection and maple syrup production. These trees are very valuable to nature and people.
Learning about maple tree health starts with knowing their special traits and growth patterns. Rock Maple, or Acer saccharum, grows well in the northeastern United States. It likes cold winters and moderate rain.
Maple Tree Life Expectancy and Growth Patterns
Maple trees can live up to 300 years. Their growth is shaped by several important factors:
- Strong root systems that help them absorb nutrients well
- They can adapt to different environments
- Their leaves change color with the seasons
Common Signs of a Healthy Maple Tree
To spot a healthy maple tree, look for these signs:
- Leaves that are bright and change color with the seasons
- Intact bark without big damage
- They grow consistently every year
- No signs of disease
Importance of Regular Tree Inspection
Checking trees regularly is key to keeping maple trees healthy. Finding problems early can stop bigger issues. These issues could affect leaf collection or maple syrup making.
“A well-maintained maple tree is not just a beautiful landscape feature, but a living ecosystem supporting wildlife and economic resources.” – Forest Health Expert
| Tree Health Indicator | Healthy Status | Warning Signs |
|---|---|---|
| Leaf Color | Vibrant green, seasonal changes | Yellowing, brown spots |
| Bark Condition | Smooth, intact | Peeling, cracks |
| Growth Rate | Consistent annual growth | Stunted or irregular growth |
By knowing these basics about maple tree health, you can help these trees live long and be productive.
Essential Guide to Maple Tree Leaves
Maple tree leaves are key for identifying different tree species. With about 128 maple species worldwide, knowing about leaf anatomy is vital. These leaves show a tree’s health, how it changes with the seasons, and how it adapts to its environment.
Maple leaves have some common traits:
- They are divided into 3-5 distinct lobes
- Leaf size usually ranges from 2-6 inches wide
- They come in unique colors depending on the species
Different maple species have amazing leaf diversity. For example:
- Red Maples: Leaves with three lobes turn a vibrant “fire-truck red” in autumn
- Sugar Maples: Leaves are broader with five lobes, showing deep orange to crimson in fall
- Silver Maples: Leaves are sharply pointed with pale silvery-green undersides
“Maple leaves are not just beautiful—they’re biological indicators of tree health and environmental conditions.”
Understanding maple leaf anatomy helps you check tree health and spot diseases. It also shows the important role these leaves play in forests. By noticing small differences in leaf structure, color, and texture, you’ll get better at identifying tree species.
Major Diseases Affecting Maple Trees
Maple trees face many diseases that can harm their health and life span. It’s important to know about these threats to protect your trees. Nature photography can help spot early signs of disease, leading to quick action.
Different maple trees are more or less prone to diseases. Some are stronger, while others need more care to stay healthy.
Verticillium Wilt: A Silent Threat
Verticillium shrivel could be a major illness influencing maple trees. It mainly hits Sugar Maple, Silver Maple, and Japanese Maple. Look out for:
- Delayed leaf development
- Branch dieback
- Brown staining beneath bark when branches are cut
Recognizing Sapstreak Disease
Sapstreak disease mainly targets sugar maples, causing a lot of damage. Infected trees may show:
- Stunted growth
- Gradual decline in overall tree health
- Potential tree removal in severe cases
Root Rot: Understanding the Underground Threat
Root rot can severely harm maple trees due to poor soil drainage and too much moisture. Key indicators include:
- Leaf discoloration
- Reduced tree vigor
- Soft, decaying roots
“Early detection is the best defense against maple tree diseases.” – Arborist Expert
| Disease | Primary Affected Maple Types | Key Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Verticillium Wilt | Sugar, Silver, Japanese Maple | Branch dieback, delayed leaf growth |
| Sapstreak | Sugar Maple | Stunted growth, tree decline |
| Root Rot | All Maple Varieties | Leaf discoloration, root decay |
Keep your maple trees healthy by watching them closely and acting fast on any disease signs. With the right care and early action, you can keep these trees beautiful and strong.
Identifying Leaf-Specific Diseases
Maple trees add beauty to landscapes but can face leaf diseases. These diseases harm their fall colors and health. Knowing about these conditions helps protect your trees by observing and taking photos.
Leaf diseases can change how your maple tree looks and feels. Here are the most common ones:
- Tar Spot: Shows as black spots up to ½ inch across, with yellow edges
- Leaf Spots: Brown spots on leaves caused by fungi
- Anthracnose: Makes dead areas on leaf edges
- Powdery Mildew: A white powdery coating on leaves in humid summers
These diseases can change how leaves turn color. For example, powdery mildew can make leaves turn color early, changing the fall look.
| Disease | Symptoms | Impact on Leaf Color |
|---|---|---|
| Tar Spot | Black spots with yellow margins | Early leaf drop |
| Anthracnose | Dead areas near leaf edges | Irregular discoloration |
| Powdery Mildew | White powdery coating | Premature fall colors |
Early detection through careful nature photography can help prevent significant tree damage.
Even though these diseases seem scary, most maple trees can bounce back. Regular checks, proper watering, and balanced fertilizing can lower disease risks.
Understanding Maple Tree Leaves and Their Common Issues
Maple trees are known for their beautiful leaves. These leaves tell us a lot about the tree’s health and how it changes with the seasons. They are more than just pretty to look at; they are key signs of the tree’s well-being.
When we try to figure out what kind of tree a maple is, we start with its leaves. These leaves change a lot throughout the year. They show us important details about the tree’s health and the environment around it.
Seasonal Color Changes
Maple leaves are famous for their amazing color changes. In the fall, they turn from green to bright reds, oranges, and yellows. These changes are not just pretty; they are a sign that the tree is getting ready for winter.
- Spring: Bright green leaves emerge
- Summer: Deep green, full canopy
- Fall: Dramatic color shifts from green to warm tones
- Winter: Leaves drop, revealing branch structure
Leaf Structure and Development
Knowing about leaf anatomy helps us spot health problems. Maple leaves are known for their unique shapes and edges. Looking at the veins, texture, and overall shape of the leaf can tell us a lot about the tree’s health.
Signs of Stress in Leaves
Stressed maple leaves show certain signs that we should watch for:
- Early color change before autumn
- Unusual spots or discoloration
- Wilting or drooping
- Premature leaf drop
“A maple tree’s leaves are its silent communicators, revealing health stories through their appearance and transformation.” – Arborist Wisdom
By paying attention to your maple leaves, you can catch diseases early. This helps keep your tree healthy and strong.
Prevention Strategies for Maple Tree Diseases
To keep your maple trees healthy, you need to act early. Knowing the special needs of each maple tree helps you care for them better. This keeps them thriving in forest ecosystems.

- Regular tree inspection and monitoring
- Proper pruning techniques
- Strategic watering practices
- Soil management
- Pest control
Pruning is key to keeping maple trees healthy. Experts say prune in late summer to cut down on sap loss and disease spread. Cutting off dead or sick branches helps air move better and stops fungi from growing.
“Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to maple tree care.” – Arborist Expert
Managing water is also vital. Maple trees need about an inch of water a week when it’s hot. Mulching keeps the soil moist and controls the temperature.
| Prevention Strategy | Benefit | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Pruning | Improves air circulation | Annually |
| Mulching | Retains soil moisture | Seasonal |
| Pest Monitoring | Reduces disease risk | Quarterly |
Knowing what each maple tree needs is important. Some trees might need extra care because of their disease risk. This targeted approach helps them stay healthy.
Using these prevention methods can make your maple trees stronger. They will stay healthy and vibrant for a long time.
Treatment Methods for Diseased Maple Trees
If your maple tree shows signs of disease, it’s important to know how to treat it. This is especially true for deciduous trees used in maple syrup production. Each disease needs a specific treatment to keep your tree healthy.
Using the right treatment can save your maple tree’s health. It also helps avoid damage to its structure and how well it produces syrup.
Chemical Treatments
Chemical treatments can be a good choice for some maple tree diseases. Here are some targeted options:
- Apply fungicides made just for maple trees
- Use copper-based treatments for fungal infections
- Implement systemic treatments that absorb through the tree’s vascular system
Natural Remedies
Natural methods offer eco-friendly ways to manage maple tree health:
- Remove infected branches and leaves
- Improve soil drainage
- Use neem oil or baking soda mixtures as organic fungicides
Professional Treatment Options
For complex maple tree diseases, professional help is sometimes needed. Certified arborists can:
- Perform comprehensive diagnostic tests
- Develop customized treatment plans
- Implement advanced preservation techniques
“Early detection and appropriate treatment are key to maintaining the health of your maple trees and preserving their potential for maple syrup production.”
Choosing the right treatment depends on the disease, the tree’s condition, and the environment. Deciduous trees like maples have unique needs.
Seasonal Care for Maple Tree Health
Caring for your maple tree needs a thoughtful plan for each season. Knowing its specific needs is key to its health. The fall season brings both beauty and challenges for maple tree owners.
In autumn, collecting leaves is vital to stop disease spread. Careful management of fallen leaves can protect your tree’s long-term health. Nature photography lovers will enjoy the colors, but taking care of the tree is just as important.
- Spring: Focus on gentle pruning and fertilization
- Summer: Monitor for signs of stress and hydration needs
- Fall: Collect fallen leaves and prepare for winter
- Winter: Protect roots and minimize potential damage
“A maple tree’s health is a year-round commitment,” says arborist experts.
Maple trees need careful care during seasonal changes. In fall, remove dead branches and gather fallen leaves to stop fungal infections. Your nature photography can show these changes while helping the tree.
Adjust watering based on temperature changes. Slowly cut back on watering as it gets cooler. Make sure the soil stays moist until it freezes. Mulching with 2-4 inches of organic material keeps roots warm and moist.
Understanding seasonal needs helps your maple tree flourish all year.
Environmental Factors Affecting Maple Tree Wellness
Knowing how different parts of the environment affect maple trees is important. These trees need the right soil, climate, and water to stay healthy. Typically, it is particularly genuine for deciduous trees like maples.

Your maple tree’s health depends on many environmental factors. These factors help it grow strong and healthy. All maple trees need similar things to thrive.
Soil Conditions and Requirements
Soil is key for maple tree health. Sugar maple trees do best in zones 3 through 8. They prefer certain soil types.
- Well-drained, slightly acidic soil (pH 6.0-7.0)
- Rich in organic matter
- Good nutrient composition
Climate Impact on Tree Health
Climate changes affect maple trees a lot. Scientists say sugar maple trees might not be in some areas soon if we don’t act.
| Climate Factor | Impact on Maple Trees |
|---|---|
| Temperature Fluctuations | Disrupt sap production cycles |
| Drought Conditions | Weaken root systems |
| Seasonal Changes | Affect leaf color and tree vigor |
Water Management Techniques
Managing water is crucial for maple trees. Drought can make trees weak.
“Water is the lifeblood of forest ecosystems, especially for delicate deciduous trees like maples.” – Forest Ecology Research Team
- Maintain consistent soil moisture
- Use mulching to retain water
- Implement deep, infrequent watering
By understanding these environmental factors, you can help your maple trees thrive and contribute to the health of broader forest ecosystems.
Professional Care and When to Seek Help
Keeping your maple trees healthy is key. Knowing when to call a pro is important. Arborists offer care that goes past fundamental upkeep.
“A skilled arborist can diagnose and treat tree issues before they become irreversible problems.” – Professional Arborist Association
When should you reach out to a tree care expert? Here are some key times:
- Persistent leaf discoloration or unusual patterns
- Visible signs of disease spreading rapidly
- Structural damage or potential tree instability
- Complex root system complications
- Preparation for maple syrup production
Finding the right arborist is crucial. Look for these credentials:
| Credential | Significance |
|---|---|
| ISA Certification | International Society of Arboriculture validation |
| State Licensing | Confirms professional training and expertise |
| Insurance Coverage | Protects against potential property damage |
Arborists know a lot about trees. They can tell the difference between maple types. They give advice that helps your trees stay healthy and boosts syrup production.
Acting fast can save your maple trees. It helps keep your syrup production going strong.
Best Practices for Long-term Maple Tree Maintenance
Keeping maple trees healthy needs a careful plan. Knowing about leaf anatomy is key to keeping these trees strong in forest ecosystems.
For your maple tree to stay healthy and live long, follow these important steps:
- Do annual health checks to spot problems early
- Prune in late spring and summer
- Don’t cut off more than 25% of live growth each season
- Watch the soil and make sure it drains well
“Proper maintenance is the key to a thriving maple tree that can enhance your landscape for decades.”
Pruning is vital for maple tree health. Experts say to use certain methods:
| Pruning Practice | Recommended Timing | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Pruning | 3-5 years after planting | Develop strong tree structure |
| Maintenance Pruning | Late spring to summer | Remove dead/diseased branches |
| Canopy Management | Every 2-3 years | Reduce long overextended limbs |
Understanding your maple tree’s needs is crucial. Regular care, watching closely, and getting expert advice can make your tree flourish for years.
Conclusion
Learning about maple tree leaves helps you protect these amazing trees. The Big Leaf Maple has leaves up to 12 inches wide. In the interim, White Maple takes off are fragile and interesting.
Nature photography lets you track your maple trees’ health. By taking pictures of their leaves, you can spot diseases early. Different maples, like Silver, White, and Big Leaf, need special care to stay healthy.
Caring for maple trees helps the whole ecosystem. When maple leaves break down, they make the soil better. This underpins numerous creatures and keeps the scene differing.
By taking good care of maple trees, you’re helping the environment. Whether you have one tree or many, your efforts are crucial. They ensure these trees will be around for a long time.
Start your maple tree care journey with excitement and commitment. With the knowledge from this guide, you’ll protect these trees and help preserve nature for future generations.
FAQ
How can I tell if my maple tree is solid?
A healthy maple tree has green leaves and strong bark. It grows consistently and shows no signs of disease or pests. Look for even leaf color, strong branches, and symmetrical growth.
Regular checks can spot problems early.
What causes maple leaf discoloration?
Leaf discoloration can come from many things. Nutrient shortages, fungal diseases, stress, bad watering, or pests can cause it. Normal color changes in the fall are okay, but sudden changes might mean a problem.
How often should I inspect my maple tree for diseases?
Inspect your maple tree at least four times a year. Check-in spring, mid-summer, early fall, and winter. Look for changes in leaves, bark, and tree shape. Experts say to do a full check-up every year.
Can maple tree diseases spread to other trees?
Yes, diseases like verticillium wilt can spread. They move through soil, roots, or air. Keep trees apart, clean tools, and avoid spreading diseases.
What is the most excellent time to gather fallen maple takes off?
Collect fallen leaves in late autumn. This stops disease spread. Use them as mulch or compost.
How do environmental factors impact maple tree health?
Soil quality, humidity, and temperature affect maple trees. Poor drainage and extreme weather can weaken them. This makes them more likely to get sick.
When should I call a professional arborist?
Call an arborist for serious problems. Look for severe leaf color changes, branch dieback, root rot, pests, or structural damage. They’re key for complex diseases.
How do different maple tree species vary in disease resistance?
Disease resistance varies among maple species. Sugar and red maples are often stronger. Japanese maples are more prone to some diseases. Knowing your tree’s type helps in caring for it.
Can I prevent maple tree diseases naturally?
Yes, natural prevention is possible. Keep soil healthy, ensure good drainage, and promote biodiversity. Use organic fertilizers and practice crop rotation. Companion planting can also help.
How does maple tree health impact maple syrup production?
Tree health affects syrup production. Healthy trees with strong bark and roots make more sap. Good care, disease prevention, and the right growing conditions improve syrup quality and quantity.