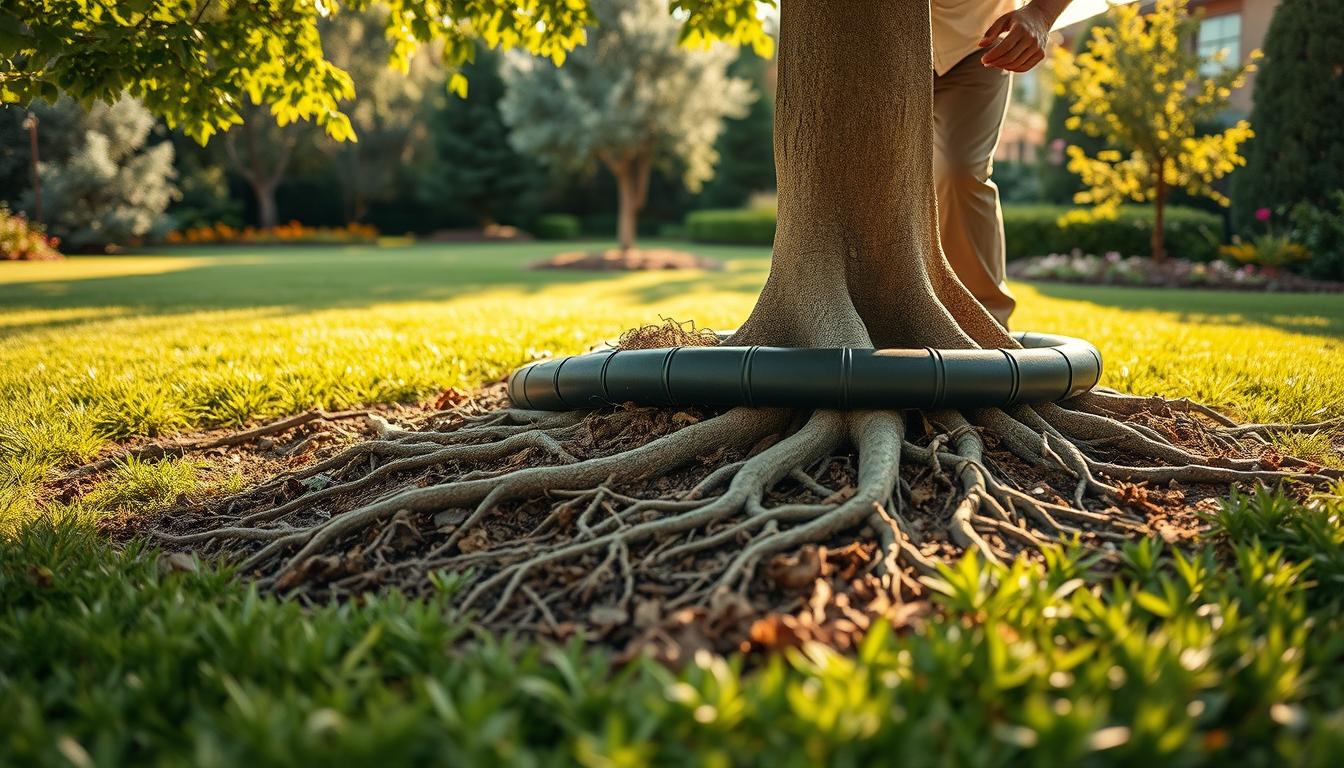
As a homeowner, you understand the beauty and shade that trees bring to your yard. However, those same trees can silently cause significant damage to your property. Invasive tree roots can wreak havoc on your lawn, sidewalks, and even underground utilities, leading to costly repairs.
A tree root barrier is a simple yet effective solution to prevent this damage. It’s a physical or chemical obstacle that directs root growth away from areas you want to protect. By installing a high-quality barrier, you can safeguard your hardscapes, soil, and underground structures from invasive roots.
Common issues caused by invasive roots include damaged foundations, cracked patios, and disrupted underground utilities. These problems can lead to expensive fixes, especially if left unchecked. However, with the right materials and techniques, you can prevent these issues before they arise.
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is one of the most robust materials for long-term root protection. Its durability ensures that your barrier remains effective for years, shielding your property from root-related damage. In this article, we’ll explore essential tips for selecting, installing, and maintaining a tree root barrier, along with real-world examples and case studies to guide you through the process.
By understanding the threats posed by root growth and implementing best practices, you can protect your property and enjoy the benefits of your trees without the associated risks. Let’s dive into the key takeaways to get you started.
Table of Contents
Understanding Invasive Tree Roots and Their Impact
Invasive tree roots can silently wreak havoc on your property, causing significant damage to lawns, sidewalks, and underground utilities. These roots, often from species like willows or silver maples, can extend far beyond the tree’s canopy, seeking water and nutrients. Their growth can undermine structures and disrupt soil stability, leading to costly repairs.
How Invasive Roots Damage Your Hardscape and Soil
Invasive roots can cause uplift and cracks in sidewalks and patios. For instance, a study showed that roots can grow up to 6 feet deep and spread 2-3 times wider than the tree’s height. This lateral growth can destabilize soil and damage underground pipes, leading to blocked drains and utility line damage. Proper installation of a root barrier, extending 18-24 inches deep for larger trees, can mitigate this risk.
Recognizing the Signs of Root Encroachment
Early detection is crucial. Look for signs like raised soil, cracked pavement, or struggling vegetation. Surface roots near the soil surface often indicate deeper issues. Regular inspections and timely action can prevent major damage, emphasizing the need for appropriate root barrier application and maintenance.
- Surface roots can extend several meters from the trunk, causing uplift and structural instability.
- Soil type and moisture influence root growth, with dry or compacted soils leading to more surface roots.
- Barrier materials like HDPE are effective in redirecting root growth, while chemical repellents can also deter encroachment.
By understanding root behavior and taking proactive measures, you can protect your property from invasive root damage, ensuring your trees coexist peacefully with your yard’s structures.
Tree Root Barrier: Essential Features and Benefits
Protecting your yard from invasive growth requires more than just cutting back. A high-quality barrier offers a long-term solution that safeguards your property while promoting healthy growth. These barriers are designed to redirect growth away from sensitive areas, ensuring your hardscapes and utilities remain undamaged.
Durable Materials and Design Considerations
Modern barriers are crafted from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), known for its exceptional durability. These barriers often feature raised ribs and ground lock tabs, which enhance stability and prevent encroachment. For instance, the 80 mil HDPE barriers from Sherrilltree and Americover are renowned for their robustness and long-term protection.
When choosing a barrier, consider materials that offer both strength and flexibility. HDPE barriers are a popular choice due to their ability to withstand harsh conditions while maintaining effectiveness over time.
Advantages Over Traditional Root Pruning Methods
Unlike traditional pruning, which requires frequent maintenance and can harm the tree, barriers provide a proactive solution. They prevent damage before it occurs, reducing the need for costly repairs. Additionally, barriers promote healthy growth by redirecting roots away from structures.
| Feature | HDPE Barrier | Traditional Pruning |
|---|---|---|
| Material | High-density polyethylene | N/A |
| Thickness | 80 mil | N/A |
| Design Features | Raised ribs, ground lock tabs | N/A |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | High maintenance |
| Longevity | Long-lasting | Short-term solution |
By installing a barrier at planting time, you can prevent future issues, ensuring your yard remains safe and visually appealing for years to come.
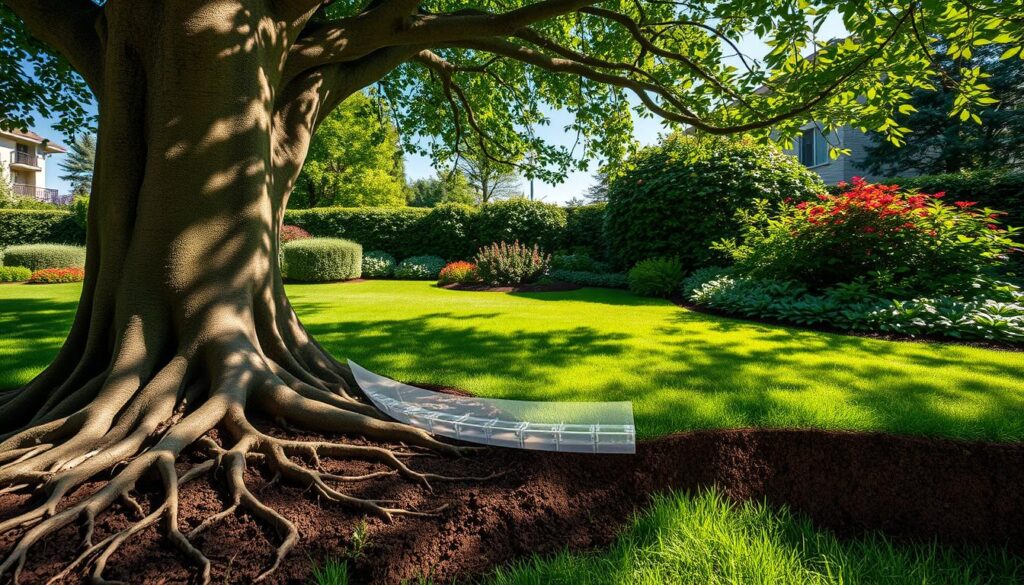

Application Techniques and Maintenance Strategies
Installing and maintaining a tree root barrier requires careful planning and execution to ensure effectiveness. Proper techniques can prevent damage to your patio, sidewalk, and curb while protecting underground utilities.
Proper Installation to Protect Your Patio and Sidewalk
To install a barrier effectively, start by digging a trench around the tree. The trench depth should be at least 12 inches for small trees and up to 48 inches for larger ones. Use a trenching shovel or backhoe for deeper trenches. Place the barrier panels securely, ensuring they extend beyond the root system.
The panels should be aligned in a linear or surround configuration based on the tree’s planting situation. For example, a surround configuration is ideal for trees in open areas, while a linear setup works best near hardscapes. Maintain a small gap between the root ball and the barrier to allow for healthy growth.
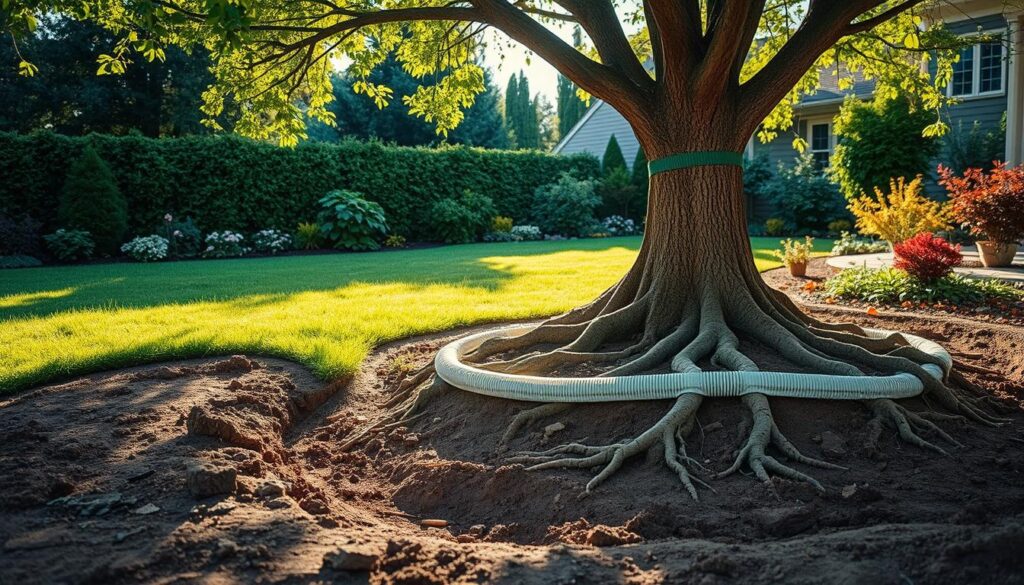

Routine Maintenance and Safe Root Pruning Tips
Regular inspections are crucial to ensure the barrier remains intact. Check for any signs of damage or root encroachment. Safe root pruning involves cutting only the necessary roots to avoid harming the tree. Use sharp tools to make clean cuts, and avoid over-pruning, as this can stress the tree.
Case studies show that proper maintenance can reduce future damage and lower maintenance costs. For instance, barriers installed around utility lines have minimized root-related issues by up to 90%. Additionally, using high-quality materials like HDPE ensures long-term durability and effectiveness.
When pruning, focus on removing dead or diseased roots. This not only protects your hardscapes but also promotes healthy tree growth. Always follow manufacturer instructions for specific product recommendations and safety guidelines.
Conclusion
Protecting your property from invasive root growth is a smart investment in its long-term health and stability. By understanding how roots grow and taking proactive steps, you can prevent costly damage to your hardscapes, utilities, and foundations.
High-quality materials, such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), offer lasting protection against invasive roots. Proper installation, including adequate depth and configuration, ensures barriers are effective. Regular inspections and maintenance are key to their longevity.
Early detection of root encroachment and timely action can save you from major repairs. By addressing issues early, you reduce the need for frequent pruning and repairs, making your property safer and more cost-efficient.
Effective application and regular maintenance make a significant difference in preserving both your yard and tree health. Consider seeking professional advice and exploring products from leading manufacturers to find the best solution for your needs.
Take the first step today and explore your options to protect your property. With the right approach, you can enjoy the beauty of your trees while safeguarding your home and outdoor spaces.
FAQ
How do I identify invasive root growth in my yard?
Look for cracks in your patio or sidewalk, uneven ground, or soil lifting. These are common signs of invasive root growth. Regular inspections can help you address the issue before it causes significant damage.
What materials are best for a root barrier?
High-density polyethylene and durable plastics are popular choices due to their strength and resistance to root penetration. These materials are designed to last and provide long-term protection for your hardscape.
Can I install a root barrier myself?
Yes, many homeowners successfully install root barriers on their own. However, for larger areas or deeper roots, it’s recommended to consult a professional to ensure proper installation and effectiveness.
How deep should a root barrier be installed?
The depth depends on the type of tree and its root system. Generally, installing the barrier 12-18 inches deep is sufficient to prevent root encroachment and protect your patio and sidewalk.
Will a root barrier harm the health of my tree?
When installed correctly, a root barrier directs root growth downward, promoting healthy tree development. It prevents invasive growth without causing harm to the tree.
What are the benefits of using a root barrier over root pruning?
Root barriers provide a long-term solution by preventing root regrowth. Unlike pruning, which may need to be repeated, a barrier offers a more permanent and maintenance-free solution.
How do I maintain a root barrier after installation?
Frequently assess the obstruction for any harm or crevices. Trim any roots that attempt to grow over the barrier to ensure their effectiveness over time.
Can a root barrier be used for newly planted trees?
Yes, installing a root barrier when planting a new tree can help guide its root growth from the start, preventing future damage to your hardscape and surrounding soil.
How long does it take to see results from a root barrier?
You can expect immediate protection from root encroachment. Over time, the barrier will continue to prevent root growth, providing ongoing protection for your yard.