Growing up in the southern United States, I remember walking through my grandfather’s pecan orchard. The pecan tree leaves rustling in the warm breeze fascinated me. These memories sparked my lifelong curiosity about these remarkable trees and their stunning foliage.
Pecan tree leaves are more than just green decorations on a tree. They represent a complex and beautiful system of botanical engineering. This system plays a crucial role in the tree’s survival. From their unique compound leaf anatomy to their environmental significance, pecan tree leaves tell a story of resilience and adaptation.
In this exploration, you’ll discover five incredible facts about pecan leaf anatomy. These facts will transform how you view these remarkable botanical wonders. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast, a gardening lover, or simply curious about the natural world, these insights will give you a newfound appreciation for the intricate beauty of pecan tree leaves.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Remarkable World of Pecan Trees
Pecan trees, found in the southeastern United States, are a key part of North American botanical history. These trees provide more than tasty nuts. Knowing about their leaves helps us see their importance in nature.
Pecan trees grow well in many places, showing their adaptability. Their leaves have details that botanists and nature lovers find interesting.
Historical Roots and Geographic Spread
Native American tribes valued pecans for food and trade. These trees grew in areas like:
- Southern United States
- Texas river valleys
- Oklahoma grasslands
- Mississippi River corridors
Economic Impact in North America
Pecan trees have a big impact on the economy. The U.S. produces over 80% of the world’s pecans. This makes them very important for farming.
| Region | Annual Production | Economic Value |
|---|---|---|
| Georgia | 130 million pounds | $320 million |
| Texas | 90 million pounds | $220 million |
| New Mexico | 45 million pounds | $110 million |
Pecan trees are not just valuable for farming. They also support many ecosystems and help local economies.
Pecan Tree Leaves: Essential Components and Structure
Exploring pecan leaf anatomy opens a world of botanical wonder. Pecan compound leaves are unique, unlike simple leaves on many trees. These complex leaves are vital for the tree’s life and growth.
The pecan compound leaves have several important parts that work together:
- Rachis: The central stem that supports multiple leaflets
- Leaflets: Individual leaf segments arranged along the rachis
- Petiole: The main leaf stalk connecting the compound leaf to the branch
Usually, a pecan leaf has 9 to 17 leaflets, giving it a feather-like look. Each leaflet is lance-shaped, with a pointed tip and smooth edges. This shows the amazing complexity of pecan leaf anatomy.
| Leaf Component | Function | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Leaflets | Photosynthesis | Elongated, 3-6 inches long |
| Rachis | Structural support | Flexible central stem |
| Petiole | Connection to branch | Allows leaf movement |
The vascular system in pecan compound leaves is incredible. Delicate veins transport water and nutrients through every leaflet. This design helps pecan trees grow well in different environments.
The Life Cycle of Pecan Foliage
Pecan trees have a fascinating journey of leaf growth all year. Knowing about pecan foliage helps us see how leaves grow. This growth is key to the tree’s health and how well it produces.
The life cycle of pecan leaves shows how the tree adapts with the seasons. Each stage is important for the tree’s growth and energy.
Spring Emergence and Development
When spring comes, pecan trees start growing leaves with great care. It begins with bud break, where small buds open up, showing off green leaves. Spring leaf growth is marked by:
- Rapid cell expansion
- Vibrant light green coloration
- Soft, tender leaf tissues
- Initial chlorophyll production
Summer Growth Characteristics
In summer, pecan leaves are at their best. The leaves’ features become more obvious as they work hard to make food for the tree.
| Summer Leaf Stage | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Full Expansion | Dark green color, maximum surface area |
| Photosynthesis Peak | High energy production, robust leaf structure |
| Moisture Adaptation | Waxy cuticle development, reduced water loss |
Fall Color Changes and Leaf Drop
Autumn brings big changes to pecan leaves. As it gets colder, the leaves turn yellow and bronze. The end of the growth cycle comes with leaf drop.
- Pigment changes from green to warm autumn colors
- Gradual nutrient reabsorption
- Protective layer formation at the leaf stem
- Complete leaf detachment
Compound Leaf Arrangement and Characteristics
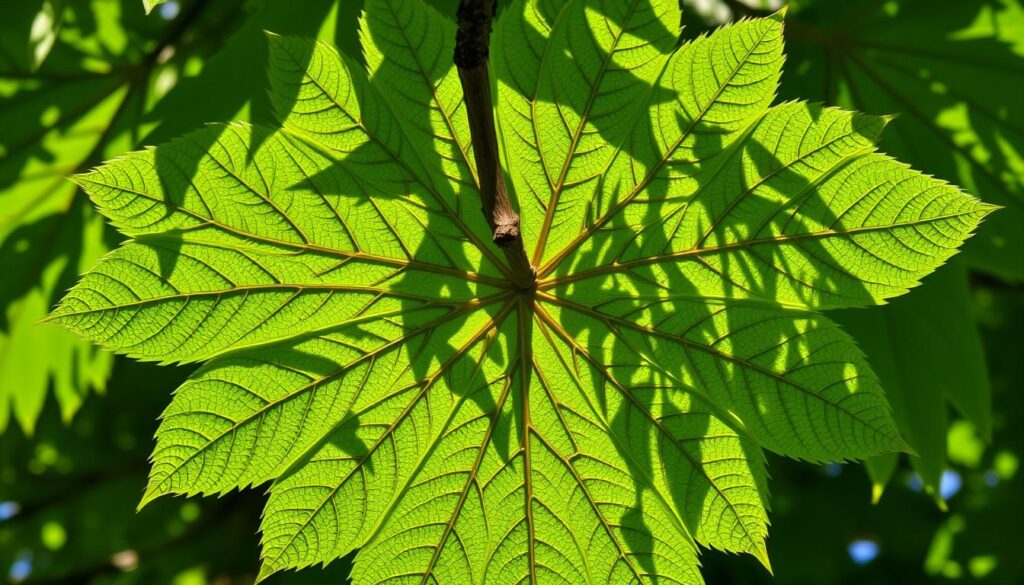

Pecan trees have a unique leaf structure that stands out. Their leaves are made up of many leaflets on a central stem. This design is both intricate and functional.
Each pecan leaf has 9 to 17 leaflets, showing off nature’s engineering skills. These leaflets are arranged in a pinnate pattern. This pattern helps the tree in many ways.
- Enhanced photosynthetic surface area
- Improved air circulation through the foliage
- Better temperature regulation
- Increased resistance to environmental stressors
Looking at pecan leaves helps us see how trees adapt. Each leaflet captures sunlight well, helping the tree stay healthy. This design also helps the tree save water, which is key in different climates.
“Nature’s design in pecan leaves is a masterpiece of functional complexity.” – Botanical Research Institute
Botanists and tree lovers are amazed by pecan leaves. They show the tree’s long history of evolution. By studying these leaves, we learn about the tree’s strength and complex biology.
Identifying Pecan Tree Leaves Through the Seasons
Pecan tree leaf identification is a fun journey for those who love nature and botany. Knowing how to spot pecan leaves helps you find these trees in different places and at different times.
Learning about pecan leaf growth stages is key. It lets you become an expert at spotting these amazing leaves.
Distinctive Features for Easy Recognition
Pecan leaves have unique traits that make them easy to spot:
- Compound leaf structure with 9-17 individual leaflets
- Alternate leaf arrangement on branches
- Lance-shaped leaflets with serrated edges
- Bright green color during the growing season
- Pinnate venation pattern
Common Look-alike Species
Some trees might look like pecans. Be careful not to confuse them with these similar leaves:
- Hickory trees most closely resemble pecan leaves
- Black walnut trees with compound leaf structures
- Butternut trees with similar leaf arrangements
Seasonal Variation Guide
Pecan leaves change a lot throughout the year. In spring, they start out as light green and soft. Summer brings full, rich green leaves. Fall shows off yellow and bronze colors before they fall off.
Pro tip: Examine leaf size, texture, and arrangement to confidently identify pecan trees in any season.
Health Benefits and Environmental Impact
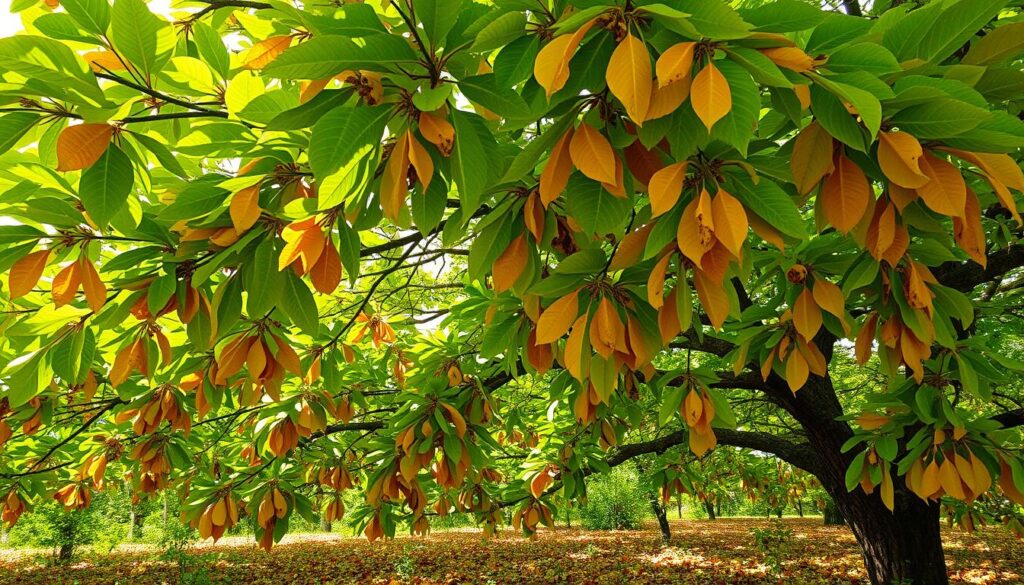

Pecan tree leaves are key to keeping our environment healthy. They do more than just look good on trees. They act as natural filters and support ecosystems that help both animals and people.
Your local pecan trees help protect the environment in many ways:
- Air Purification: Pecan leaves are great at pulling in carbon dioxide and pushing out oxygen
- Wildlife Habitat: Leaves offer shelter and food for many animals
- Soil Nutrient Cycling: When they break down, they make the soil richer in minerals
- Temperature Regulation: Their dense leaves help cool the area around them
The benefits of pecan tree leaves go beyond just their immediate area. Pecan tree leaves create micro-ecosystems that support biodiversity. Insects, birds, and small mammals rely on these leaves for survival. This creates complex food webs that keep ecosystems balanced.
“Pecan trees are nature’s silent guardians, working tirelessly to maintain environmental health through their incredible leaf systems.” – Ecological Research Institute
By supporting pecan trees, you help the environment. Their leaves are a natural way to improve air quality and protect habitats. They are essential for managing landscapes in a sustainable way.
Common Diseases Affecting Pecan Leaves
Pecan leaf diseases can harm your trees’ health and productivity. Knowing about these issues helps protect your trees and keep them healthy.
The structure of pecan leaves is key to spotting and fighting infections. Different diseases affect different parts of the leaf. This creates unique signs that help you catch problems early.
Bacterial Infections in Pecan Leaves
Bacterial infections can severely damage pecan leaves. Some major bacterial diseases include:
- Bacterial leaf scorch
- Xanthomonas leaf spot
- Bacterial blight
Fungal Diseases Threatening Pecan Leaves
Fungal infections are another big threat to pecan trees. Important fungal diseases are:
- Downy spot
- Powdery mildew
- Cercospora leaf spot
| Disease Type | Primary Symptoms | Potential Damage |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Leaf Scorch | Brown leaf edges | Reduced photosynthesis |
| Downy Spot | Yellow-brown spots | Premature leaf drop |
| Powdery Mildew | White powdery coating | Weakened leaf structure |
Prevention and Treatment Strategies
To keep your pecan trees safe from diseases, you need to act early. Regular inspection, proper pruning, and keeping your trees healthy are key steps.
If you see signs of disease, talk to a local agricultural office. They can give you specific advice for your area and tree type.
Pest Management for Pecan Foliage
Keeping your pecan trees safe from pests is key. Knowing how pecan leaves work helps you fight pests better. This keeps your trees healthy and productive.
Pecan leaf pests can harm your trees a lot. They include small bugs and tiny creatures that hurt the leaves.
- Aphids: Tiny sap-sucking insects that damage leaf tissues
- Webworms: Caterpillars that create protective webs on leaves
- Leaf miners: Larvae that tunnel through leaf surfaces
- Scale insects: Small creatures that attach to leaf surfaces
Using integrated pest management is the best way to protect your trees. It mixes different methods to reduce pest harm and keep the tree’s ecosystem balanced.
| Pest Control Method | Effectiveness | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Biological Controls | High | Low |
| Chemical Treatments | Immediate | Moderate |
| Cultural Practices | Preventative | Very Low |
Finding pests early is very important. Regular checks help spot problems before they get worse. This saves your pecan leaves.
Prevention is always more cost-effective than treating a full-blown pest invasion.
Experts suggest a complete plan. It includes using natural enemies, targeted treatments, and caring for the trees. This keeps them strong and healthy.
Proper Care and Maintenance for Healthy Leaves
To keep pecan tree leaves vibrant, you need to care for them well. Knowing the growth stages helps you give your tree the best care. This ensures your tree stays healthy and strong.
Good care starts with understanding how to keep your tree healthy. This means looking at many important parts of tree health.
Watering Requirements
Watering is key for growing pecan leaves. Your tree needs steady moisture, especially when it’s growing fast.
- Water deeply once per week
- Provide 1-2 inches of water per irrigation
- Adjust frequency during dry or rainy seasons
Fertilization Guidelines
Feeding your tree the right nutrients is vital. Good fertilization helps leaves grow strong and the tree stay healthy.
| Season | Recommended Nutrients | Application Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Spring | Nitrogen-rich fertilizer | 2-3 lbs per inch of trunk diameter |
| Summer | Balanced NPK blend | 1-2 lbs per mature tree |
| Fall | Potassium supplement | 1 lb per mature tree |
Pruning Techniques
Pruning is important for healthy leaves and growth. Trimming right helps with air and sunlight.
- Remove dead or diseased branches
- Prune during dormant winter months
- Use clean, sharp pruning tools
- Cut at 45-degree angles near branch collars
By following these care tips, you’ll grow strong pecan trees with healthy leaves.
Conclusion
Exploring pecan tree leaves opens a world of complexity and importance. Learning about their anatomy shows us the amazing life of these trees. Each leaf is more than just a part of the tree; it shows the health of the tree and how it adapts to its environment.
The details of pecan tree leaves show their incredible strength. They help the tree make food, protect it, and adjust to changes. Whether you love gardening, botany, or nature, knowing about pecan leaves can make you appreciate these trees even more.
By taking good care of pecan trees and knowing how to handle diseases and pests, you help them thrive. This knowledge helps you grow healthy trees that are good for local ecosystems and farms in the U.S.
Understanding pecan tree leaves is more than just looking at them. It connects us to nature and shows how each leaf is vital for the tree’s life. As you learn more about these trees, remember that each leaf has a story of strength, adaptation, and beauty.
FAQ
What makes pecan tree leaves unique?
Pecan tree leaves are special because they have a compound leaf structure. They usually have 9-17 leaflets on a central rachis. This design helps the tree photosynthesize better and adapt to different environments.
How do pecan leaves change throughout the year?
Pecan leaves go through a beautiful change. In spring, they start out as bright green. By summer, they grow fully and help the tree make food. In autumn, they turn golden-yellow before falling off.
What are the most common diseases affecting pecan tree leaves?
Pecan leaves can get sick with diseases like bacterial leaf scorch, anthracnose, and powdery mildew. These diseases can make the leaves turn colors, spots, and even fall off, harming the tree.
How can I identify a pecan tree by its leaves?
Look for long, compound leaves with 9-17 lance-shaped leaflets. They measure 12 to 20 inches in length, with individual leaflets ranging from 4 to 7 inches long. In summer, they’re dark green, and in autumn, they turn yellow-brown.
What pests commonly attack pecan tree leaves?
Pests like pecan leaf phylloxera, webworms, and aphids often harm pecan leaves. They eat the leaves, make webs, or suck sap, weakening the tree.
How often should I water my pecan tree to maintain healthy leaves?
Water your pecan tree deeply but not too often. Give it 1-2 inches of water per week in the growing season. Adjust based on rain and soil moisture to avoid overwatering.
Do pecan leaves have any environmental benefits?
Yes, pecan leaves are very beneficial. They clean the air, provide homes for wildlife, make oxygen, and improve soil health when they break down.
What nutrients do pecan leaves need to stay healthy?
Pecan leaves need nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients like zinc and magnesium. Fertilizing them right keeps them green and healthy.
Can I propagate a pecan tree from a leaf?
No, you can’t grow a new pecan tree from a leaf. You can graft, bud, or grow from seeds. Leaves are important for photosynthesis, but they can’t start a new tree.
How do I protect my pecan tree leaves from pest damage?
Use a mix of methods to protect your pecan tree leaves. Monitor them often, encourage good bugs, keep the tree healthy, and use treatments like horticultural oils or biological controls when needed.